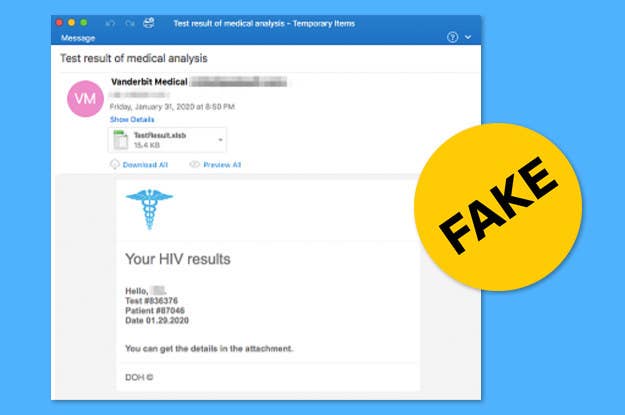
Hackers are sending emails with fake HIV results and coronavirus information that infect computers with malware, according to research from cybersecurity research firm Proofpoint.
The fake HIV emails are designed to look like they come from Vanderbilt University, possibly to exploit the credibility of the Vanderbilt University Medical Center. The emails, which include an attached spreadsheet labeled “test results,” have been sent to insurance, health care, and pharmaceutical companies. When downloaded, a user is prompted to install macros, which leads to them becoming infected with malware known as the Koadic Remote Access Trojan.
“It’s really the lure with the HIV test results and the use of a health university, that's really the thing that's interesting about this,” Sherrod DeGrippo, senior director of the threat research and detection team at Proofpoint, told BuzzFeed News.
The HIV test phishing attack emerged in late January, roughly the same time Proofpoint and other cybersecurity firms began tracking hackers using coronavirus-themed emails to infect computers. Some of the COVID-19 emails promoted fake cures and other conspiracies.
The emails targeted industries such as manufacturing, transportation, health care, and higher education. Proofpoint has had to create special tracking for malicious COVID-19 emails for the first time.
“Coronavirus has been exhausting for us,” DeGrippo said.
Hackers are evolving their coronavirus messaging in line with the global response. Knowing that many companies asked employees to work from home, the hackers send emails that claim to be from company HR departments or executives. The victim would be asked to sign into DocuSign or Microsoft Word, which is when their credentials would be stolen.
They also spoofed the World Health Organization and targeted Italians once the outbreak worsened in that country.
“Italy's prominence within the coronavirus epidemic has caused the shift of it in the lure languages and geotargeting,” she said.
The HIV and coronavirus emails are effective because they inspire curiosity or fear in recipients, according to DeGrippo. “If they don't get [you with] one emotion, they're going to get the other one,” she said.
The Koadic malware used for the HIV phishing attacks gives hackers access to a computer and allows them to consider their next steps as they learn more about their victim. The next phase of the attack may come months after the initial infection. It could be ransomware, a banking trojan, or information theft. Kodiac is widely used in Eastern Europe and has been deployed by Russia, China, and Iran, though there’s no evidence any of those countries are behind this new attack.
To protect yourself from phishing, DeGrippo recommends using unique passwords across accounts, multifactor authentication, running regular virus scans on your computer, and being skeptical of emails from unfamiliar sources that trigger an emotional reaction.
“Using these really highly emotionally charged lures is becoming the standard,” she said. “We're just starting to see a move away from the shipping receipts and the invoices and the resumes into a trend of big emotional scare tactics and curiosity starters.”
